The fascinating world of industry provides a glorious host of modern equipment with which manufacturers use to build and finish an array of products, including those of ceramics, plastics and steel. As technology has advanced so much over time, it becomes easy to forget how greatly it has evolved, inevitably shaping industrial trends to the stage which they are at today.
The much-larger scale industrial ovens which are used in industry are designed to cope with huge operations for long amounts of time, creating considerable quantities of heat and pressure, (requiring the implementation of appropriate and ideal safety measures, including heat extraction and necessary safety guidelines for the workforce).
Industrial ovens are spacious heated chambers which are used in the process of curing or finishing batches of products simultaneously. Other processes include drying and baking; each process whereby the product manufacturing process is finalised, rendering them ready for resale. This is the absolute final phase of the products’ manufacturing procedure.
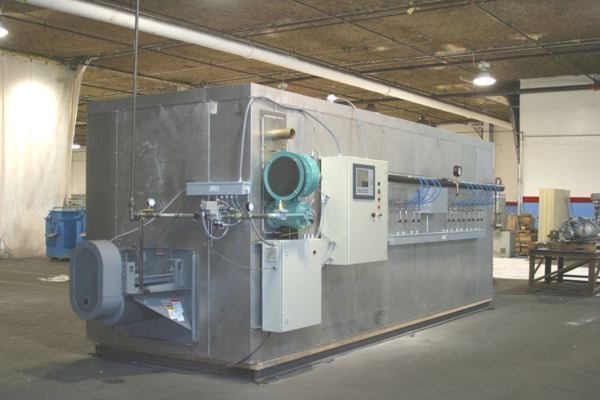

It is also common to see industrial ovens being used for numerous other applications than the above mentioned, such as chemical processing, food production and even electronics. For instance, circuit boards are passed through a conveyor oven to attach surface mount components.
The batches of products which are processed at any given time vary depending on the process required, and also the scale of the company and operation. Other factors which differ immensely are temperature ranges, configurations and size. For instance, aircraft components are also finished in extremely high temperature environments, where an automatic control system holds air temperature at steady value of 2°F. Commonly, in the more modern versions of industrial ovens, it is now possible to automate levels of temperature within the oven, specific to each product requirement. This is of utmost use for science lab technicians working on different chemicals, and also for manufacturing specifications of individual products.
The laboratory uses of industrial ovens cover a broad spectrum, with techniques and processes such as sterilization of chemicals or substances and the drying of glassware specific to laboratory experiments. Sufficient air circulation is achieved through a turbine or air pushed through a powerful fan also used for fume abatement. Certain ovens such as convection ovens are used for various testing procedures, such as thermal and evaporation trials.
Industrial drying ovens are probably the most used type of oven in industry…specifically engineered to eradicate any excess moisture which is produced through the manufacturing processes involved in many products’ cycle, or for necessary moisture removal for certain experiments. The key principle of industrial drying ovens is that a pre-determined quantity of controlled air is continuously pushed through an exhaust, effectively being replaced with fresh air and avoiding the danger of any build-up of chemicals and pressure.
By Sam Hurley
(Junior Digital Marketing Consultant at FDC)